The heart is a pump that pushes blood through the body. Blood consists of solids and liquid. The basic function of the blood is to transport dissolved or suspended materials to a location of usage or a location of disposal. The liquid portion of the blood is made up of water with mineral ions and bioactive molecules dissolved in it; it is called plasma. It is sort of a salt-water solution with extras, in a very simplified view. The solid portion of blood is made of cells, platelets, cell fragments, and very large molecules. The ratio of these two components, solid and liquid, is expressed as a percentage and is called the hematocrit.
We can easily determine hematocrit with a centrifuge. Simply spin a clotted tube of blood at many times the force of gravity (about 12,000 or so times earthly gravity) and the solid portions of the blood will settle to the bottom of the tube. The liquid portion will remain at the top of the tube. Some simple math — divide the height of the solid portion of the sample by the total height of the sample then multiply by 100 — provides a percentage that will normally be around 45% for men and 35% for women. The precise proportion of solid to liquid in blood is plastic, changing in response to simple internal or external environmental changes to maintain the body’s homeostatic balance. Values below normal variance are called anemia. Values higher than normal variance are called polycythemia.
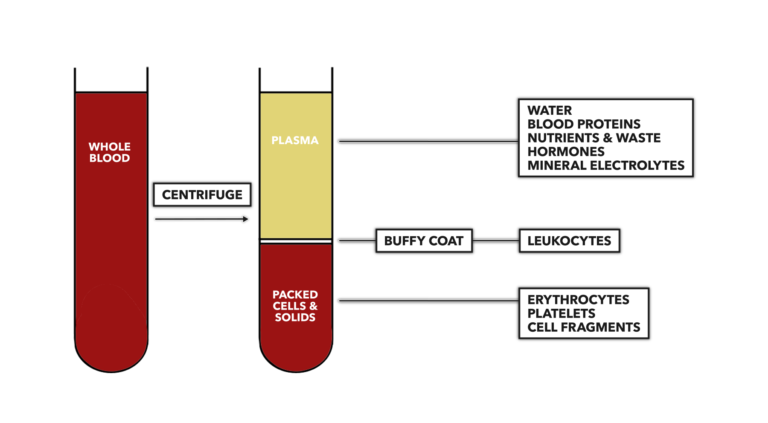
Figure 1: Determination of the hematocrit. Measure the height of the solid portion of the blood (bottom portion of right tube) then divide by the total height of the column of blood (distance between top line of plasma and bottom line of solids). When separated, water comprises approximately 90% of plasma volume. Dissolved mineral electrolytes in plasma, such as sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, chloride, and bicarbonate, make up less than 1% of its volume.
There are two basic types of blood cells: red blood cells and white blood cells. Red blood cells are more accurately called erythrocytes. They are red in appearance because they possess a substantial iron content. White blood cells are called leukocytes.
Red Blood Cells
Red blood cells, about 25 trillion of them, primarily carry oxygen to tissues that need it and carbon dioxide to the lungs for removal. The number of erythrocytes can vary, but a higher number of erythrocytes (a higher hematocrit) carries with it a functional benefit that can lead to a higher ability to transport and consume oxygen. A higher hematocrit is associated with better endurance performance. As exemplified throughout human anatomy, a simple and small morphological change produces a profound functional improvement. As such, a great deal of interest has been directed toward developing exercise protocols to increase hematocrit, and unfortunately (in specific reference to sport), toward developing artificial means of increasing it.
In the latter case, using artificial means to increase hematocrit for sport performance enhancement, particularly when hematocrit is elevated to the 60s or higher, has resulted in heart failure during training. Essentially, the blood viscosity after drug administration, further increased during exercise, was too thick to pass effectively through small vessels.
Determining hematocrit is often a first-level doping test for endurance sports. If an athlete’s hematocrit is 50% or higher, they are generally not allowed to run, bike, or swim in competition. Further testing will then be performed on an elevated hematocrit sample to determine if the hormone erythropoietin was used to artificially increase red blood cell numbers.
White Blood Cells
Leukocytes are white because they do not contain significant amounts of iron. The blood contains far fewer leukocytes than erythrocytes. During hematocrit analysis, leukocytes aggregate as a thin fragile layer on top of the solid portion of the sample called the “buffy coat.” There are about 4,000 to 11,000 leukocytes in a microliter of blood, or about 38 billion in circulation (note that some leukocytes are found elsewhere in the body, not just in circulation).
Leukocytes do not provide exercise performance benefits other than to provide infection surveillance and defense services that keep you ready to train. In general, leukocytes produce antibodies or engulf (phagocytosis) and destroy (lysis) foreign matter. They can also participate in other important physiological processes. There are five basic types of leukocytes:
Neutrophils – Engulf and destroy foreign matter, about 66% of total leukocytes
Lymphocytes – Produce antibodies, about 23% of total leukocytes
Monocytes – Engulf damaged cells and foreign pathogens, about 6% of total leukocytes
Eosinophils – Important in the allergic response, about 3% of total leukocytes
Basophils – Important in the allergic response, less than 1% of total leukocytes
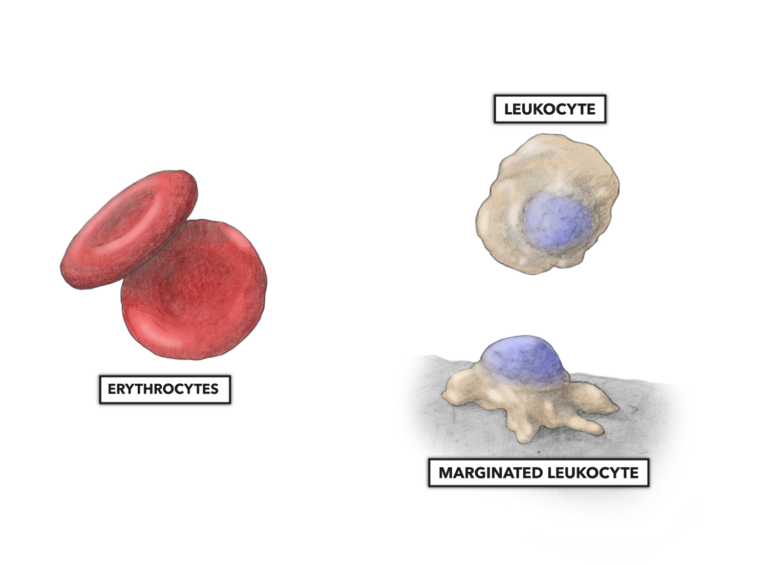
Figure 2: Erythrocytes (red blood cells) have an anucleate biconcave disk of about 8 micrometers in diameter. Leukocytes (white blood cells) have an ameboid appearance with a prominent nucleus. Each subtype of leukocyte varies by physical size (lymphocytes are about 7-10 micrometers, and monocytes are up to 25 micrometers), cytoplasmic volume, and nucleus appearance. Within the circulatory system, most leukocytes are free flowing (above right). A few are marginated, loosely adhering to and rolling along the interior wall of the blood vessel.
Exercise-Induced Changes in the Blood
In the early 1900s, it was found that hard exercise or physical labor performed in the early stages of poliovirus infection increased the severity of the infection and subsequent mortality rate. This marked the origin of the theory of exercise-induced immune suppression. It is not a surprise that attitudes toward engaging in hard exercise were not particularly positive until after a vaccine for the poliovirus was created in the 1950s. In fact there are numerous publications from that time referring to hard exercise as harmful.
More recent research into exercise-induced changes in the blood is quite ambiguous regarding changes in leukocyte morphology and function. Various frequencies and intensities of exercise can produce diverse effects on leukocyte numbers, and additional research is needed to determine specifics with regard to the positive and negative effects of exercise on the body’s immunological response.
Additional Reading
- The Heart, Part 1: Location & Orientation
- The Heart, Part 2: Muscular Organization
- The Heart, Part 3: Muscular Composition & Arrangement
- The Heart, Part 4: Conductive Pathway
- The Heart, Part 5: Blood Flow
- The Heart, Part 6: Blood Vessel Basics
- The Heart, Part 7: Coronary Circulation
- The Heart, Part 8: Systemic and Pulmonary Circulation
Comments on The Heart, Part 9: Blood
If your hypothesis of hyperthermia induced viral increased infectivity is correct then why? Lol. Our bodies increase in core temperature which helps to slow viral transcription rates. What factor during hyperthermia is increased to allow an increase in viral production? Does it relate to decreased immune system? Or increase in glucocorticoid production? Just trying to learn more. Thanks.
Regarding the last bit about exercise and immune stuff, was it ever determined why hard exercise increased the severity of the poliovirus?
Chris,
I left that bit nebulous as there are several competing theories, all based on not very strong data. Even my data is not specifically and precisely applicable to humans and to viruses across the board, but I found it intriguing (a long time ago);
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15362323/
Thanks for reading and taking time to pose a question.
Cheers,
Lon
This year I catched more infections than usual, and was surprised about it, because I thought I was somewhat healthy.
After doing some research (online) it seems that high intensive training leaves an open window (low immune system). But this seems to be truer for the intensity of an endurance athlete (aka volume). Low intensive training doesn’t seem to have an impact on white blood cells. While weightlifting has an impact on white blood cell production.
Some studies also suggest that with more experience, you can handle more volume. And that performance in CrossFit can be maintained for two days in a row. (Compared to the statement of endurance athletes this suggests to me, that too much training without according recovery does not only reduce performance but also the immune system)
I guess it’s like, you run really fast, then the next day, you don’t want to run at all, but in long term you will be able to run faster because of the training. Or you can run two days in a row, but maybe not three. So, I guess, your immune system catches on the stress, then must have a recovery phase, then gets stronger with time and exercise. (like muscle grow or any other physical adaptation)
So, I guess, I was over trained at some points this year. And the most important point to me as a father of three; next time my kids get sick, I will remember not to train at high intensity and then sleep next to them. (sidenote: Carbohydrates uptake after training (and sleep) also seems to be important for faster recovery. Not only for muscle grow, but also for immune system).
I think this is interesting in relation to the common recommendation to do “low intensive” training. Because, short term, it seems to be safer. Which unfortunately also means to “stay weaker” in the long term. The “open window” could instead be closed with proper awardness, accurate recovery and lowering of infection risks. Maybe also important for elder athletes in CrossFit.
(hope this makes sense as it is the result of my online research of the last three days)
The Heart, Part 9: Blood
4