“In the last few years, new insights have made it possible to visualize the manner in which upper-body obesity connects to glucose intolerance, hypertriglyceridemia and hypertension, with hyperinsulinemia being the key intermediary. … This article examines these insights and propose (sic) an overall hypothesis for their interrelationships, with the hope that greater awareness of the critical role of upper-body obesity will increase attention to the need to prevent it or, failing that, to correct it.” (1)
In this paradigm-shifting 1989 paper, Dr. Norman Kaplan argues that the frequent coexistence of obesity, hypertension, glucose intolerance (predecessor to diabetes) and hypertriglyceridemia (predecessor to heart disease) suggests a shared pathogenesis, specifically “insulin resistance with hyperinsulinemia, long recognized as a metabolic derangement of obesity.”
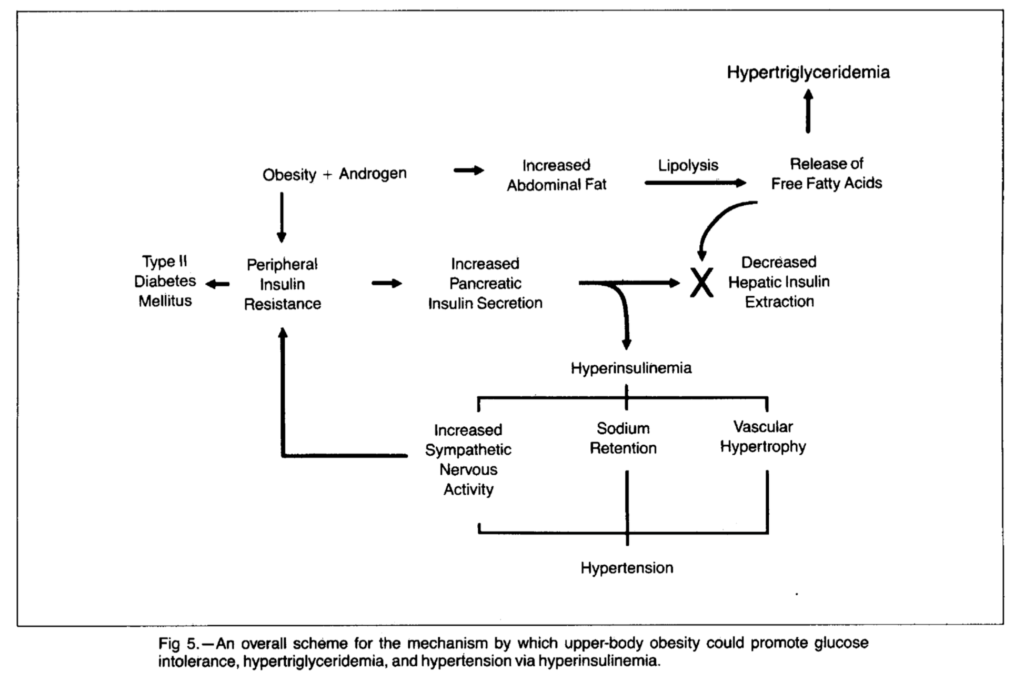
From “The Deadly Quartet: Upper-Body Obesity, Glucose Intolerance, Hypertriglyceridemia, and Hypertension” by Norman Kaplan.
Kaplan notes that upper-body obesity (abdominal obesity) is more closely related to metabolic disorders than general obesity. He further illustrates how abdominal fat leads to hyperinsulinemia as the pancreas secretes greater amounts of insulin to regulate glucose levels as insulin resistance develops. The resulting hyperinsulinemia subsequently induces hypertension through its effects on the kidneys, nervous system and vasculature. Finally, larger abdominal fat stores release free fatty acids that lead to hypertriglyceridemia while further worsening hyperinsulinemia through effects on the liver.
Kaplan thus presents this “Deadly Quartet” as a single metabolic pathway that begins with increased upper-body obesity and peripheral insulin resistance and leads to heart disease, diabetes and hypertension. He notes, in conclusion, that interventions which improve insulin sensitivity—including weight loss via certain diets (high-carbohydrate diets are specifically argued against) and exercise—might be the most effective tools to manage and prevent each and all of these conditions.