Approximately 422 million people around the world have diabetes (95% have Type 2 diabetes). The disease increases the likelihood of eventual limb amputation, blindness, heart attack, and stroke, and is one of the leading causes of kidney failure. In 2019, 1.5 million people died from diabetes.
But you don’t have to be one of them. Whether you have Type 1, Type 2, or prediabetes, you have the power to feel and move better, live longer and stronger, and thrive despite your diagnosis.
Start by getting the facts with resources from the CrossFit archives below. Get inspired by the stories we shared last week of those who’ve faced diabetes and won. Then call your local affiliate — the first step toward achieving life-changing health.
A Food-Based, Low-Energy, Low-Carbohydrate Diet for People With Type 2 Diabetes in Primary Care
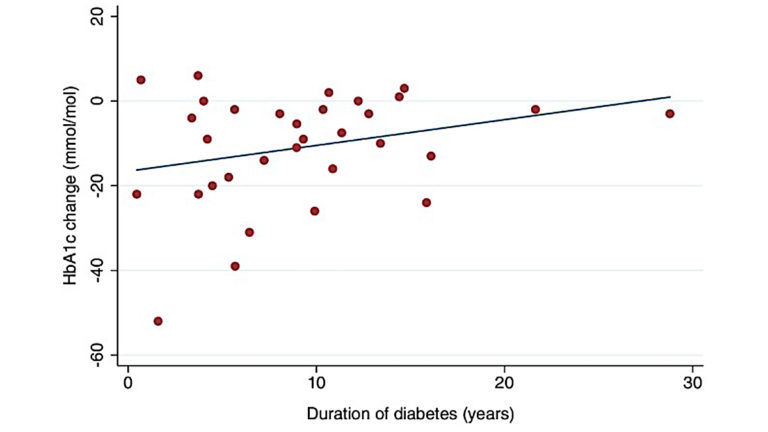
Growing evidence suggests diabetes is not a lifelong, progressive condition and dietary changes alone can lead to diabetes control and remission.
Diabetes: What It Is and Why You Need to Know About It (Even if You Don’t Have It)
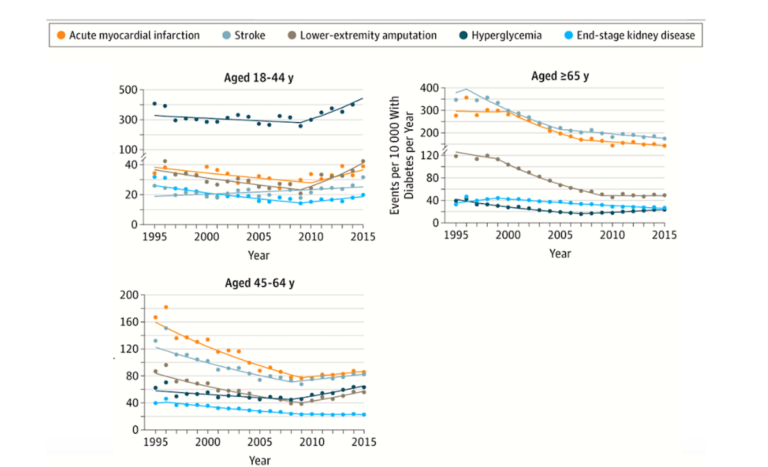
Diabetes can be a terrible disease, a disruptor of many lives, a major cause of blindness and amputations — and the suffering is made worse by the fact that for many, there is a cure, a cure resisted by the medical profession.
Diabetes, Part 3: Insulin, the Obesogenic Hormone
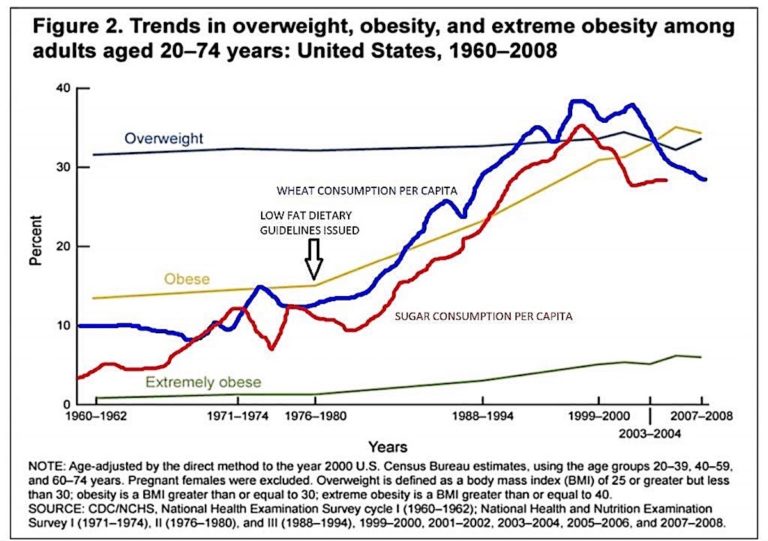
Although it is true that Type 2 diabetes is far more common in obese individuals, this does not mean that obesity is a cause of Type 2 diabetes. Correlation does not mean causation. … All of this means raised insulin levels are most likely an important cause of obesity/Type 2 diabetes rather than the other way around. The obesity that results in susceptible individuals worsens the underlying insulin resistance, thereby leading to frank Type 2 diabetes.
Prediabetes: Your Final Warning

Lifestyle changes — specifically diet and exercise — are the most effective at lowering blood sugar to a healthy level. As Dr. David Cavan, director of policy and programs at the International Diabetes Federation in Belgium, explains, “Whether you go up or down that curve is very closely related to lifestyle.”
Sugar and Diabetes: Myths and Misleadings

“In the Western world, the increase in Type 2 diabetes does correlate very well with the big increase in obesity that has occurred. But if we go to some places in Asia, or in the Far East, or in Africa, a large number of the cases of Type 2 diabetes are occurring in people who are either not overweight or they are not significantly overweight, so we have to find an explanation that is not just calories.” —Dr. David Cavan, director of policy and programs at the International Diabetes Federation in Belgium.
Dr. Lustig: Type 2 Diabetes Is “Processed Food Disease” (Full Interview)

Dr. Robert Lustig is an endocrinologist and professor of pediatrics in the Division of Endocrinology at the University of California-San Francisco. In this video, he explains sugar’s toxicity, outlines the stakes of sugar consumption, and offers suggestions for addressing the ongoing sugar crisis. “Sugar is toxic,” Lustig explains. “It proffers a set of biochemical alterations that are detrimental to human health — unrelated to its calories.”
Additional Educational Resources
- Nutrition Brief: Insulin and Blood Sugar Regulation
- Journal Club: Insulin and Exercise
- Diabetes and Carbohydrate Restriction: Where Are We Now?
- Diabetes, Part 1: Disease Models
- Diabetes, Part 2: The Causal Role of Raised Insulin
- A Different Perspective on the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes
- A Different Perspective on Treatment of Type 1 Diabetes
- Exercise and Type 2 Diabetes: New Prescription for an Old Problem
- Diabetes: Have We Got It All Wrong?
- Dietary Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus in the Pre-Insulin Era
- Type 2 Diabetes: Treating Not Managing
- Diabetes Is a Risk Factor for the Progression and Prognosis of COVID‐19
- Insulin Therapy Increases Cardiovascular Risk in Type 2 Diabetes
- The Relationship of Sugar to Population-Level Diabetes Prevalence: An Econometric Analysis of Repeated Cross-Sectional Data
- COVID‐19 and Diabetes Mellitus: Unveiling the Interaction of Two Pandemics
- The Link Between Depression and Diabetes: The Search for the Shared Mechanisms
- Reversal of Type 2 Diabetes: Normalisation of Beta Cell Function in Association With Decreased Pancreas and Liver Triacylglycerol
- Impact of Metformin on Exercise-induced Metabolic Adaptations To Lower Type 2 Diabetes Risk
- Low Carbohydrate Diet To Achieve Weight Loss and Improve HbA1c in Type 2 Diabetes and Pre‐Diabetes
- Hypothesis: Could Excessive Fructose Intake and Uric Acid Cause Type 2 Diabetes?
- Association of Blood Glucose Control and Outcomes in Patients With COVID-19 and Pre-Existing Type 2 Diabetes
- Alzheimer’s Disease and Diabetes: Insulin Signaling as the Bridge Linking Two Pathologies
- A Low-Carbohydrate High-Fat Diet Initiated Promptly After Diagnosis Provides Clinical Remission in Three Patients With Type 1 Diabetes
- Role of Insulin Resistance and Diabetes in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
- High Intensity Intermittent Exercise Improves Cardiac Structure and Function and Reduces Liver Fat in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes
- Effectiveness and Safety of a Novel Care Model for the Management of Type 2 Diabetes at 1 Year
- Sugar, Uric Acid, and the Etiology of Diabetes and Obesity
13,000 Ports in the Storm, Part 2: Educational Resources on Diabetes